
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Here’s a breakdown of core concepts and main components:
🔹 Core Concepts
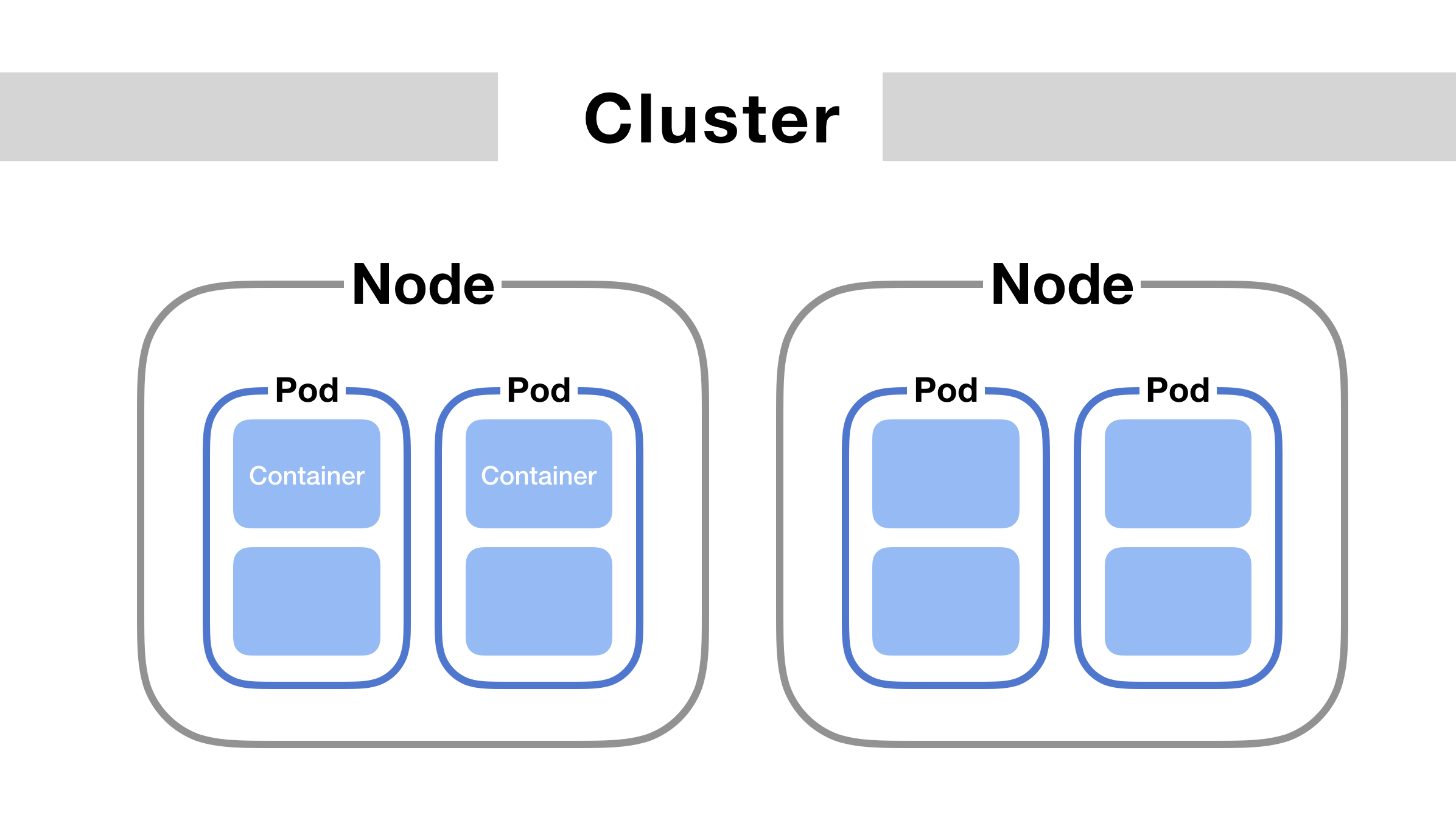
- Cluster
A set of machines (nodes) running Kubernetes. It consists of a control plane and worker nodes. - Node
A physical or virtual machine in the cluster that runs pods. There are:- Master/Control Plane node (manages the cluster)
- Worker node (runs the application workloads)
- Pod
The smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. A pod contains one or more containers with shared storage, network, and specifications. - Container
A lightweight, standalone, executable software package that includes everything needed to run a piece of software. - Service
An abstraction that defines a logical set of pods and a policy to access them—usually to enable network access across pods. - Deployment
A controller that manages pod replicas and ensures the desired number of them are running at all times. - Namespace
A way to divide cluster resources between multiple users or teams (useful for multi-tenancy).
🔧 Main Components
Kubernetes consists of two main nodes: Master & Worker.
Master node manages, plans, schedules, and monitors nodes.
Worker nodes host application as containers.
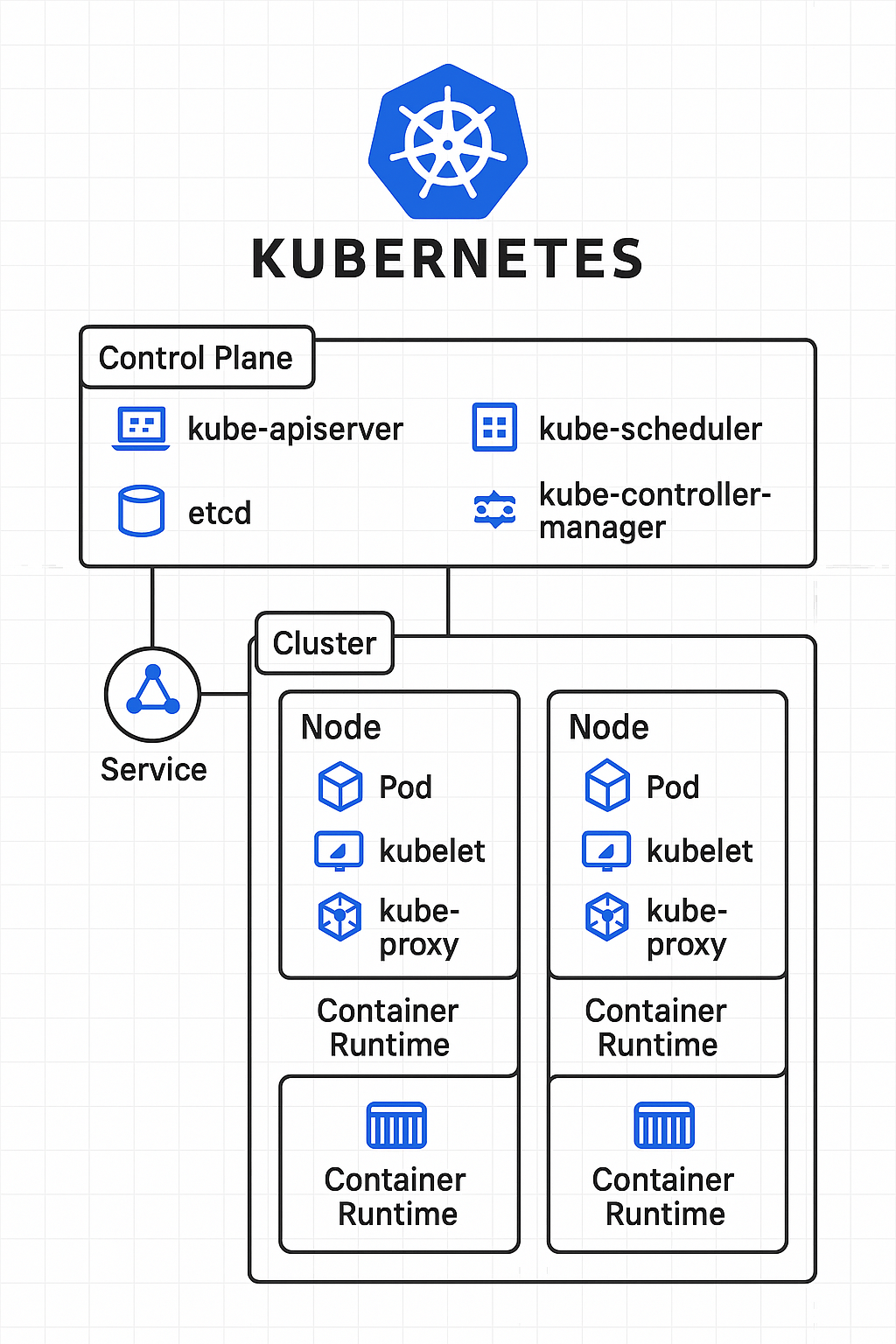
🚀 Control Plane Components
These manage the Kubernetes cluster.
- kube-apiserver
The front end of the Kubernetes control plane. It exposes the Kubernetes API. - etcd
A distributed key-value store used for storing all cluster data. - kube-scheduler
Assigns pods to nodes based on resource availability and policies. - kube-controller-manager
Runs controller processes (e.g., replication controller, node controller, etc.) to handle routine tasks. - cloud-controller-manager (optional)
Manages cloud-specific control logic (e.g., load balancers, volume storage, etc.).
⚙️ Node Components
- kubelet
An agent that runs on each worker node and ensures containers are running in a pod. - kube-proxy
Maintains network rules on nodes and handles network traffic to and from pods. - Container Runtime
The software used to run containers (e.g., Docker, containerd, CRI-O).
참고 자료
- Kubernetes Node Vs. Pod Vs. Cluster: Key Differences
Powered by. ChatGPT
'CS > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kubernetes] Scheduling(2) (0) | 2025.04.04 |
|---|---|
| [Kubernetes] Scheduling(1) (0) | 2025.04.04 |
| [Kubernetes] Service (1) | 2025.03.28 |
| [Kubernetes] Replicaset & Deployment (1) | 2025.03.27 |
| [Kubernetes] YAML (1) | 2025.03.27 |

Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration platform that automates the deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Here’s a breakdown of core concepts and main components:
🔹 Core Concepts

- Cluster
A set of machines (nodes) running Kubernetes. It consists of a control plane and worker nodes. - Node
A physical or virtual machine in the cluster that runs pods. There are:- Master/Control Plane node (manages the cluster)
- Worker node (runs the application workloads)
- Pod
The smallest deployable unit in Kubernetes. A pod contains one or more containers with shared storage, network, and specifications. - Container
A lightweight, standalone, executable software package that includes everything needed to run a piece of software. - Service
An abstraction that defines a logical set of pods and a policy to access them—usually to enable network access across pods. - Deployment
A controller that manages pod replicas and ensures the desired number of them are running at all times. - Namespace
A way to divide cluster resources between multiple users or teams (useful for multi-tenancy).
🔧 Main Components
Kubernetes consists of two main nodes: Master & Worker.
Master node manages, plans, schedules, and monitors nodes.
Worker nodes host application as containers.

🚀 Control Plane Components
These manage the Kubernetes cluster.
- kube-apiserver
The front end of the Kubernetes control plane. It exposes the Kubernetes API. - etcd
A distributed key-value store used for storing all cluster data. - kube-scheduler
Assigns pods to nodes based on resource availability and policies. - kube-controller-manager
Runs controller processes (e.g., replication controller, node controller, etc.) to handle routine tasks. - cloud-controller-manager (optional)
Manages cloud-specific control logic (e.g., load balancers, volume storage, etc.).
⚙️ Node Components
- kubelet
An agent that runs on each worker node and ensures containers are running in a pod. - kube-proxy
Maintains network rules on nodes and handles network traffic to and from pods. - Container Runtime
The software used to run containers (e.g., Docker, containerd, CRI-O).
참고 자료
- Kubernetes Node Vs. Pod Vs. Cluster: Key Differences
Powered by. ChatGPT
'CS > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Kubernetes] Scheduling(2) (0) | 2025.04.04 |
|---|---|
| [Kubernetes] Scheduling(1) (0) | 2025.04.04 |
| [Kubernetes] Service (1) | 2025.03.28 |
| [Kubernetes] Replicaset & Deployment (1) | 2025.03.27 |
| [Kubernetes] YAML (1) | 2025.03.27 |
